Therefore In Quadrant II, cos(θ) 0, sin(θ) > 0 and tan(θ) 0 (Sine positive) For an angle in the third quadrant the point P has negative x and y coordinates Therefore In Quadrant III, cos(θ) 0, sin(θ) 0 and tan(θ) > 0 (Tangent positive) For an angle in the fourth quadrant the point P has positive x coordinate and negative y coordinateStart studying Sin, cos, tan (all 4 quadrants) Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsFind the Other Trig Values in Quadrant I cos(s)=3/4 Use the definition of cosine to find the known sides of the unit circle right triangle The quadrant determines the sign on each of the values
Misc 10 Sin X 1 4 Find Sin X 2 Cos X 2 Tan X 2 Chapter 3
Quadrant 1 2 3 4 sin cos tan
Quadrant 1 2 3 4 sin cos tan-Jan 30, · Find sin x/2, cos x/2 and tan x/2, if tan x = 4/3, x in quadrant II asked Sep 26, 18 in Mathematics by AsutoshSahni ( 526k points) trigonometric functionsIn the fourth quadrant, from 270° to 360° y is negative but x is positive Thus the sign of the sine, cosine and tangent of an angle changes according to the size of the angle, that is the sign depends on which quadrant the angle is in The graphs of the three ratios, sine, cosine and tangent are shown in Figures 1, 2 and 3


Ex 3 2 Q3 Cot X 3 4 X Lies In Third Quadrant
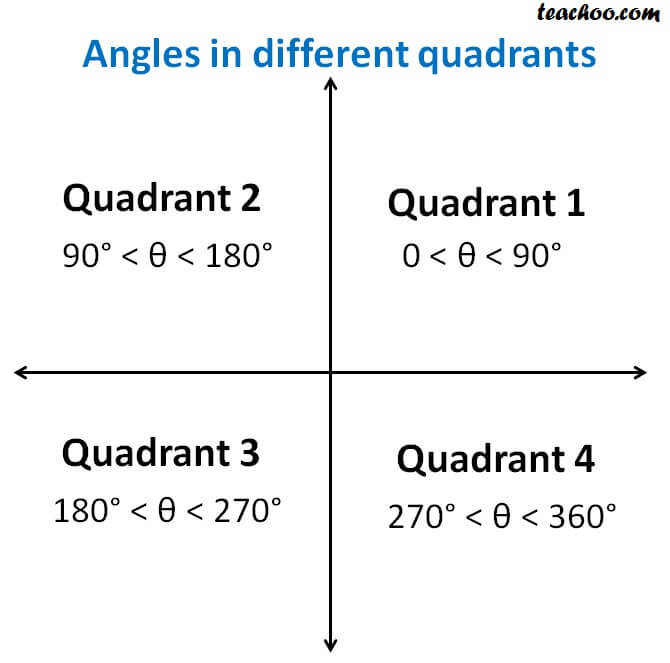
The signs of cosine in the coordinate quadrants Deriving the signs for the cosine The cosine of angle α is the abscissa of point М (x of point М) on the trigonometric circle formed by the rotation of radius vector OM by angle α This definition follows from determining the cosine through a triangleTan(θ) = 3/4, θ in Quadrant III, sin(ϕ) = − (3sqrt 10)/10, ϕ in Quadrant IV Pre Calc Find cos 2A if tan A=5/12 and trig Angle θ lies in the second quadrant, and sin θ = 3/5 Find cos θ and tan θ You can view more similar questions or ask a new questionMay 29, 18 · In Quadrant 2, angles are from 90 to 180° In Quadrant 3, angles are from 180° to 270° In Quadrant 4, angles are from 270 to 360° To learn sign of
Given, tan x =3/4 and x lies in 2nd quadrant From that were are sure about the coordinate position ie (x,y)=(4,3) From pythagoras theorem, Then, cos x=b/h Cos x=4/5 We knew, cos x= 2 (cos x/2)^2 1 * 4/5 1 =2( cos x/2)^2 * 1/10 = (cosx/2)^2 HA) quadrant 2 or 3 b) Quadrant 2 sin , cos , tan Quadrant 3 sin , cos , tan c) 115°, 245° 13 14 Answers may vary For example, given P (x, y) on the terminal arm of angle , sin , cos , and tan 15 a) 25°, 155°, 5°, 335° b) 148°, 352 o c) 16°, 106 o, 196 o, 286 o 16 a) could lie in quadrant 3 or 4 5 233° or 307° b) could lieFeb 22, 18 · 2 Sin, Cos and Tan of Sum and Difference of Two Angles by M Bourne 2 If `sin α = 4/5` (in Quadrant I) and `cos β = 12/13` (in Quadrant II) evaluate `cos(β − α)` This is not the same as Example 2 above This time we need to find the cosine of the difference Answer
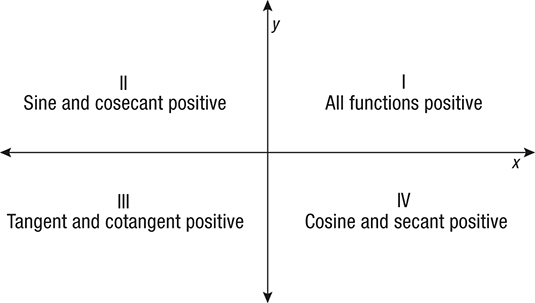
I'm having issues understanding as to how to go about doing this I cant seem to figure out how to find the values of sin and tan in terms of the given cos value in the 3rd quadrant Thanks with any and all help $\cos\theta = \frac{4}{5}$ and theta is in the 3rd quadrant, find the exact values of (i) $\sin\theta$ (ii) $\tan\theta$Apr 15, · Sine and cosecant are positive in Quadrant 2, tangent and cotangent are positive in Quadrant 3, and cosine and secant are positive in Quadrant 4 Also to know is, what quadrants are the trig functions positive and negative?Mar 14, 21 · Bicycle ramps made for competition (see Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)) must vary in height depending on the skill level of the competitors For advanced competitors, the angle formed by the ramp and the ground should be \(\theta\) such that \(\tan \theta=\dfrac{5}{3}\)


Trigonometry Quadrant Formulas



Sine Cosine And Tangent In The Four Quadrants Teachablemath
In this chapter, we have evaluated trigonometric functions at various angles, but what if we need to know what angle yields a specific sine, cosine, or tangent value?10 r ( x, y) θ O y x Definition 21 Trigonometric Functions of a General Angle Let θ be an angle in standard position and suppose that ( x , y ) is any point other than ( 0 , 0 ) on the terminal side of θ(Figure 23)If r = x2 y2 is the distance between ( x, y ) and ( 0 , 0 ), then the six trigonometric functions of θ are defined by Using similar triangles, you can see that the valuesClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Find sin x2, cos x2, tan x2 in second quadrant, if tan x = 43


Cochranmath Primary Values


What Is All Students Take Calculus In Trig Studypug
Sine is negative in Quadrant IV, and sin ˇ 3 = p 3 2, so sin 5ˇ 3 = p 3 2 The angle 5ˇ 4 is in Quadrant III, where tangent is positive Its reference angle is 5ˇ 4 ˇ= 5ˇ 4 4ˇ 4 = ˇ 4 Since tan ˇ 4 = sin ˇ 4 cos ˇ 4 = 1= p 2 1= p 2 = 1, we have tan 5ˇ 4 = 1 3 Larger angles the formulas method The second method for evaluating theSine, Cosine and Tangent in Four Quadrants The point (12,5) is 12 units along, and 5 units upHelp your child succeed in math at https//wwwpatreoncom/tucsonmathdocIf tanx= 3/4 and angle x is in quadrant 3 find tan 2x?



The Unit Circle Reference Angles And Trigonometry Ppt Video Online Download


Given Sin A 2 5 And In Quadrant Ii Find 5 Trig Function Values Youtube
When angle a is in Quadrant 3 (between 180° and 270°), both the adjacent and the opposite side are negative Hence, Sine and Cosine are negative and since Tangent (T) is a division between two negative numbers, it is the only trigonometric function that is positive Sine, Cosine and Tangent in Quadrant 4If cos 0 = 3/4 and 0 in the 4th quadrant, find the exact value of the 5 other trig values opposite side of reference right triangle in quadrant IV =√(4^23^2)=√(169)=√7Get an answer for 'Calculate cos a if sin a = 2/3 and a is in the second quadrant' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotes


The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl



Graphing Secant And Cosecant Worksheet Answers Nidecmege
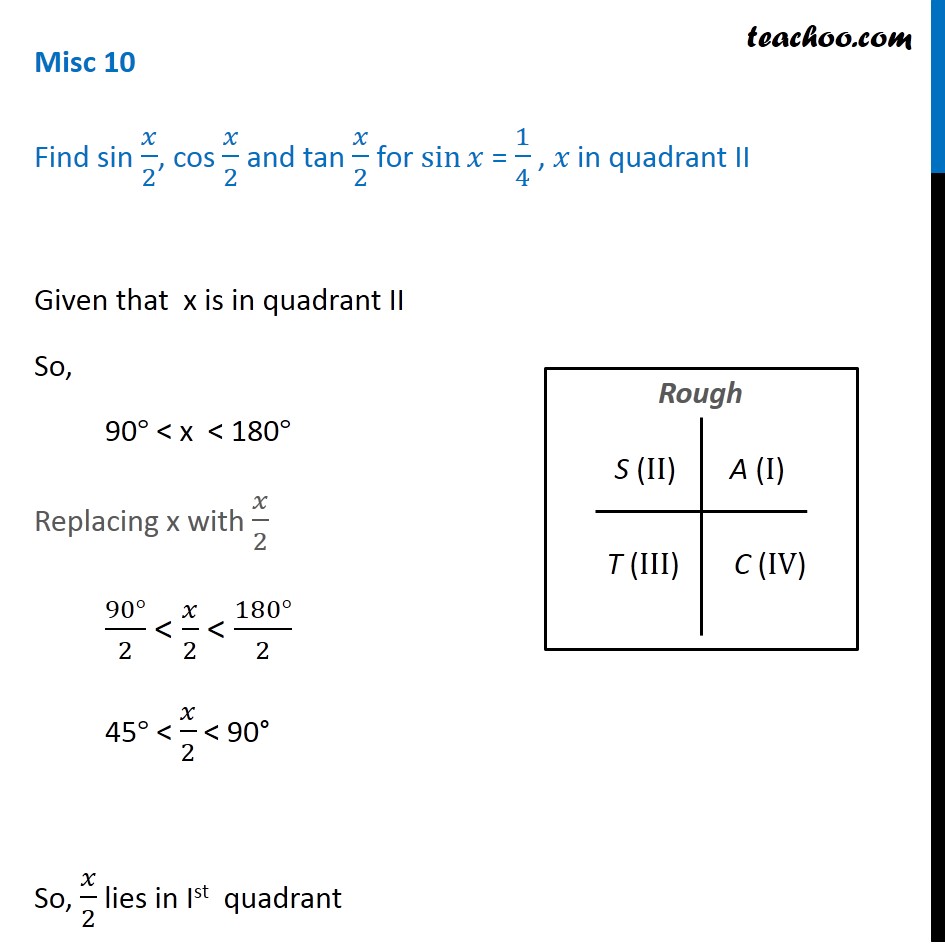
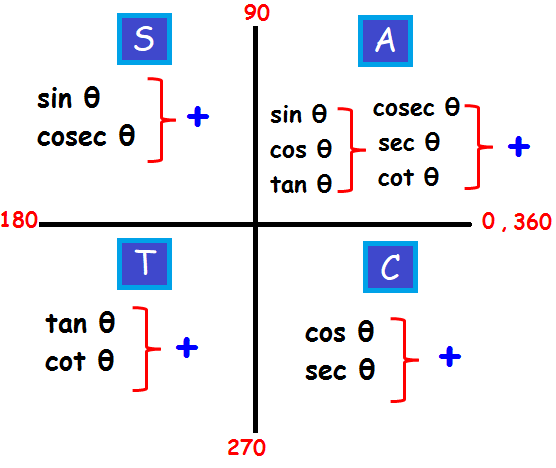
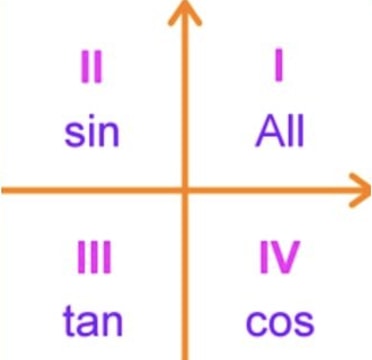
Feb 13, · Misc 10 Find sin 𝑥/2, cos 𝑥/2 and tan 𝑥/2 for sin𝑥 = 1/4 , 𝑥 in quadrant II Given that x is in quadrant II So, 90° < x < 180° Replacing x with 𝑥/2 (90°)/2 < 𝑥/2 < (180°)/2 45° < 𝑥/2 < 90° So, 𝑥/2 lies in Ist quadrant In Ist quadrant, sin , cos & tan are positive sin 𝑥/2 ,1 Given that is in Quadrant 3 and cos(a) 5 give an exact answer for the following a sin(2a) bcos() c tan(2a) 2 Given that B is in Quadrant 4 and sin(8) = give an exact answer for the following a sin(28) b cos(28) c tan(28) Decimal approximations are not allowed for this problem • Enter your answer in exact formApr 03, 16 · All the trig functions are positive in Quadrant 1 Sine and cosecant are positive in Quadrant 2, tangent and cotangent are positive in Quadrant
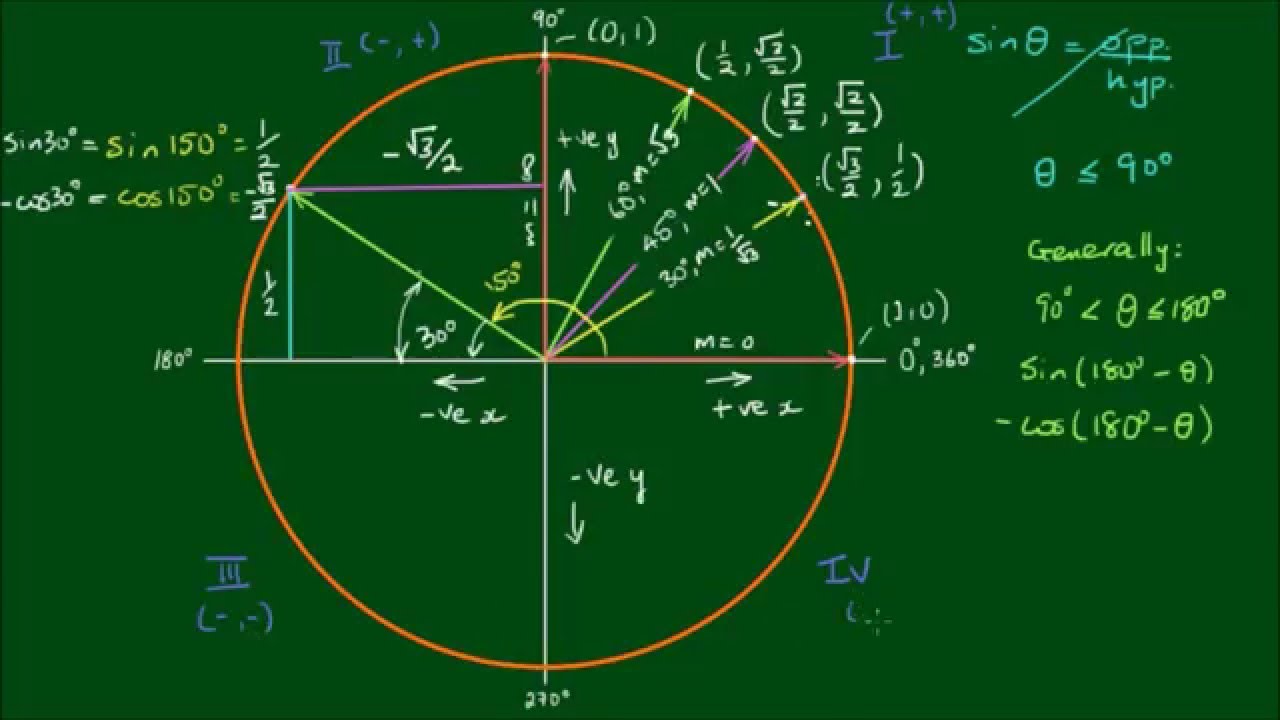


Sin Cos Tan And The Unit Circle Youtube



Content The Four Quadrants
Trigonometry (from Greek trigōnon, "triangle" and metron, "measure") is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of trianglesMay 23, 10 · Now, cos(x) = 2/3, as we've seen A positive value for cos means that x must be in either quadrant 1 or quadrant 4 Tan is positive in quadrant 1, but negative in quadrant 4Apr 23, 16 · sin(θ − ϕ);
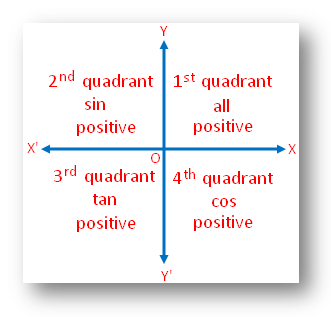


All Sin Tan Cos Rule Signs Of Trigonometrical Ratios Trigonometric Ratios
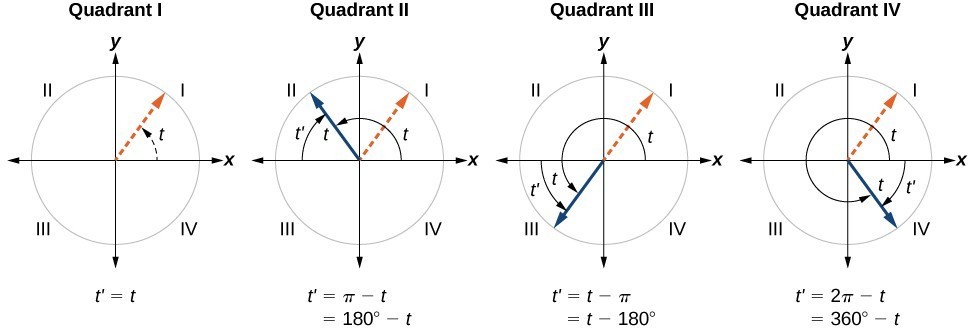


Section 4 4 Reference Angles Precalculus
You can put this solution on YOUR website!Start studying Unit Circle (All 4 Quadrants) Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsJan 26, 21 · Summary First Quadrant All are positive in this quadrant Second Quadrant Only sin is positive in this quadrant Third Quadrant Only tan is positive in this quadrant Fourth Quadrant Only cos is positive in this quadrant We now consider angles in cartesian plane


The Trigonometry Functions



Solved Without Using A Calculator Compute The Sine Cosi Chegg Com
Apr 29, 21 · Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeFind the Other Trig Values in Quadrant IV tan(t)=3/4 Use the definition of tangent to find the known sides of the unit circle right triangle The quadrant determines the sign onVisit wwwhelpyourmathcom/65 Free Math Open Educational Resources


Quadrant


Ex 3 2 3 If Cot X 3 5 Find Values Of Other Trigonometric
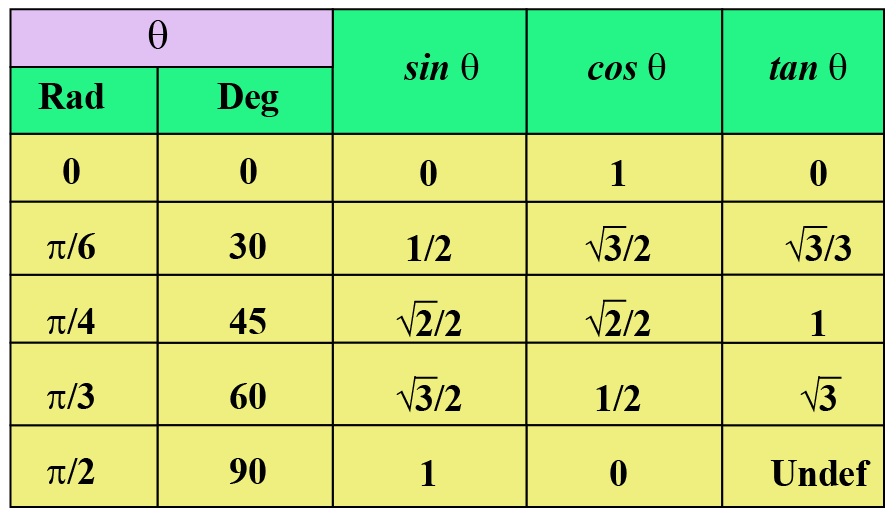
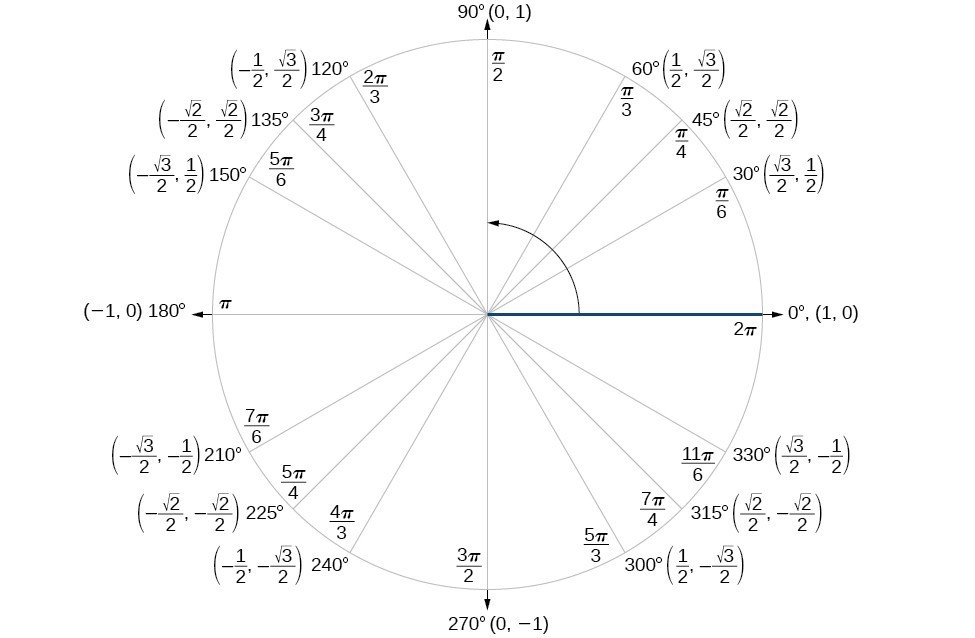
View Table of sin cos tandocx from BIO 13 at Henry Ford College Degree Radian Quadrant 00 0 300 π/6 1 450 π/4 1 600 π/3 900 Sin Cos xaxis 0 1/2 Tan Csc 0 =0 1 1 Sec 1 =undefined 0 Cot 1 =1 1 1 =2 –150° 3 45° 4 240° 5 tan = 6 cot =1 p 4 1 13 = 13 3 p 6 x2 y2 = 1 x2 y2yx y x r x y x y tan ¨ = opp adj = y x cos ¨ = adj hyp = x r sin ¨ = opp hyp = y r A = 1 2 1 2 bh h a = sin ¨ = 1 = c2 c2 = a2 b2 c2 = a2 c 2 b2 c 1sin ¨22 1cos ¨22 = a a c b 2 a b c b 30 x 10 x 15 = = 5 4 13 L 269 m PB = d B cos ı = dCAST still goes counterclockwise but starts in quadrant 4 going through quadrants 4, 1, 2, then 3 ACTS still starts in quadrant 1 but goes clockwise going through quadrants 1, 4, 3, then 2 Sines and cosines of special angles Sines and cosines of common angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90° follow the pattern with n = 0, 1, , 4 for sine


Ex 3 2 Q3 Cot X 3 4 X Lies In Third Quadrant



Domain And Range Of Trigonometric Functions Videos Solved Examples
Since we know the angle is in quadrant II, the tangent will be negative and sine will be positive Thus we can apply the proper signs as we go From Pythagoras we get math\ \sin^2{\theta}\ \ \cos^2{\theta}\ =\ 1\ /math, or,math\ \sin^2{\thAug 19, 18 · If A lies in the second quadrant and 3 tan A 4 = 0, then the value of 2 cotA – 5 cos A sin A is equal to asked Aug 16, 18 in Mathematics by AsutoshSahni ( 525k points) trigonometric functions1) Find sin θ if cos θ = 2 3 and θ is in quadrant IV 1) 2) Find tan θ if sin θ = 3 4 and s is in quadrant II 2) 3) Find sin θ if sec θ = 8 5 and tan θ < 0 3) 4) Find csc θ if cot θ = 35 and θ is in quadrant II 4) 5) Find sin θ if tan θ = 5 12 and cos θ > 0 5)



If Sin A 3 4 Then Cos A And Tan A Are Equal To What Quora



If Tan Theta 3 4 And Theta Is Not In First Quadrant Then Sin Pi 2
Solution for 13 in quadrant 48 con 46 sin e in quadrant II 47 sine 13 51 sin e 3' 4 cone 50, sin 52 cos e tan e>0 54 cse3, SA sece2 sin eQuestion Find tan(st) if cos s = (1/5), sin t = 3/5, and s and t are in quadrant 2 I have ready substituted values into the tan sum identity, but I'm having trouble with the arithmetic Answer by lwsshak3() (Show Source)To find angles, we need inverse trigonometric functions Example 45 If \(\cos(\theta)=04\text{,}\) in which quadrants



Content The Four Quadrants


Section 4 4 Reference Angles Precalculus
1) 2) Given a, b in Quadrant 11 with sin a1/3 and cos b =1/4 find tan(ab) write the function in the form C(sin x θ) f(x)2sin x 2 cos x Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our precalculus problem solver and calculatorClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ tanx = 4/3 , x in quadrant II Find the value of sinx/2, cosx/2, tanx/2 Join / Login > 11th > Maths > Trigonometric Functions > Graphs of Trigonometric Functions Find the value of sin 2 x , cos 2 x , tan 2 xTherefore, if we want to find the sine, cosine and tangent of \(128^{\circ},\) then we should find the sine, cosine and tangent of \(52^{\circ}\) and apply the appropriate positive or negative sign Example 1 Quadrant II


Act Trigonometry The Complete Guide



Trigonometry Sign For Sin Cos And Tan Quadrant


How Do You Find Sin Cos Tan Sec Csc And Cot Given 4 4 Socratic



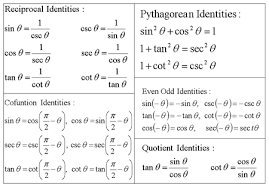
5 1 Fundamental Trig Identities Sin 1cos 1tan 1 Csc Sec Cot Csc 1sec 1cot 1 Sin Cos Ppt Download
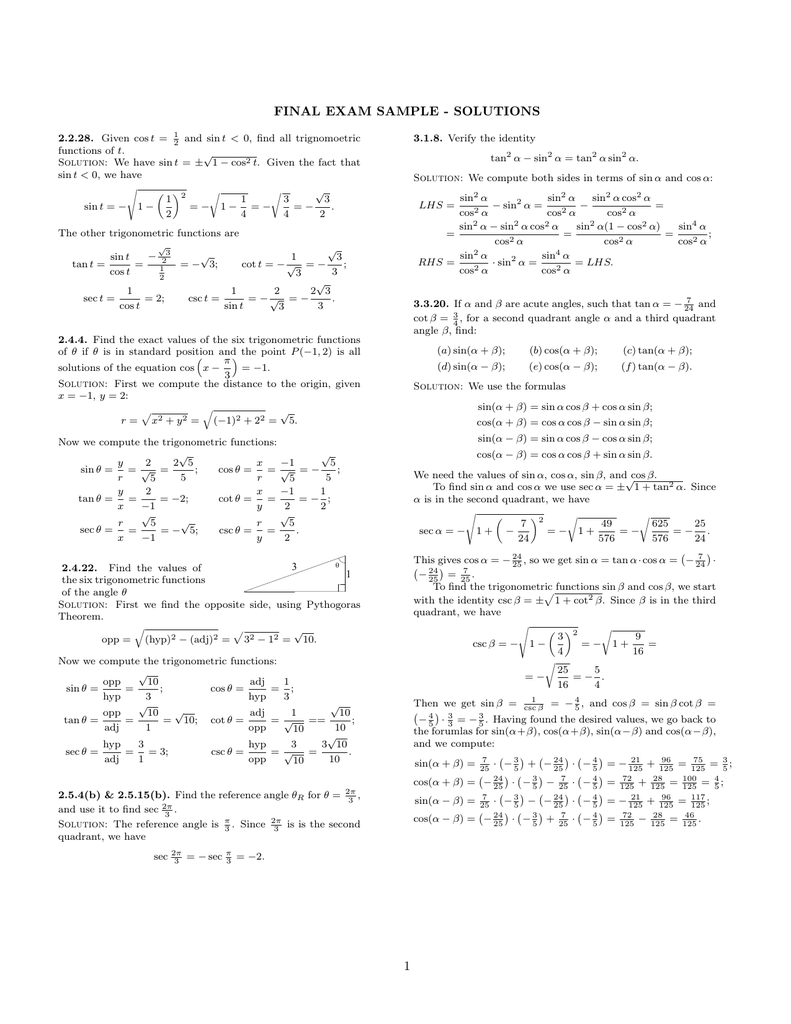


Final Exam Sample



1 E The Trigonometric Functions Exercises Mathematics Libretexts



If Sin A 3 4 Then Cos A And Tan A Are Equal To What Quora
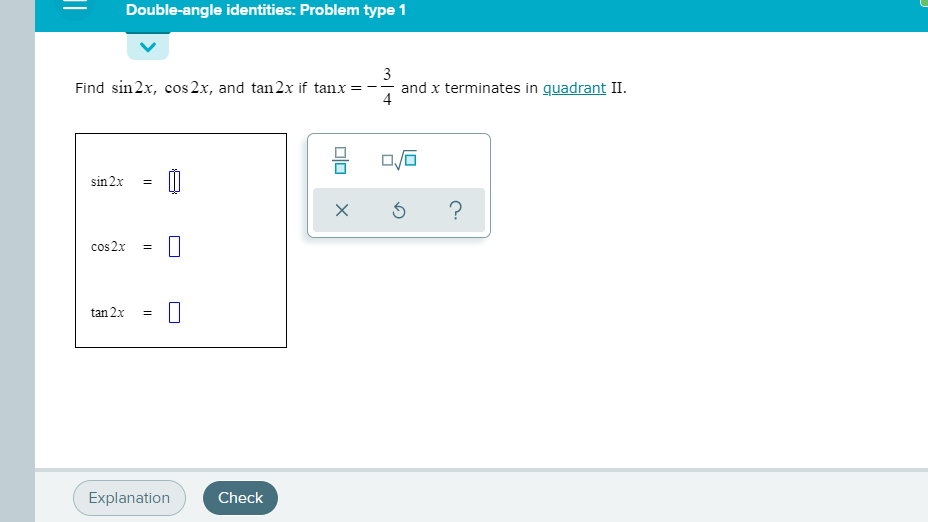


Solved Find Sin2x Cos2x And Tan2x If Tanx 3 4 And X Ter Chegg Com
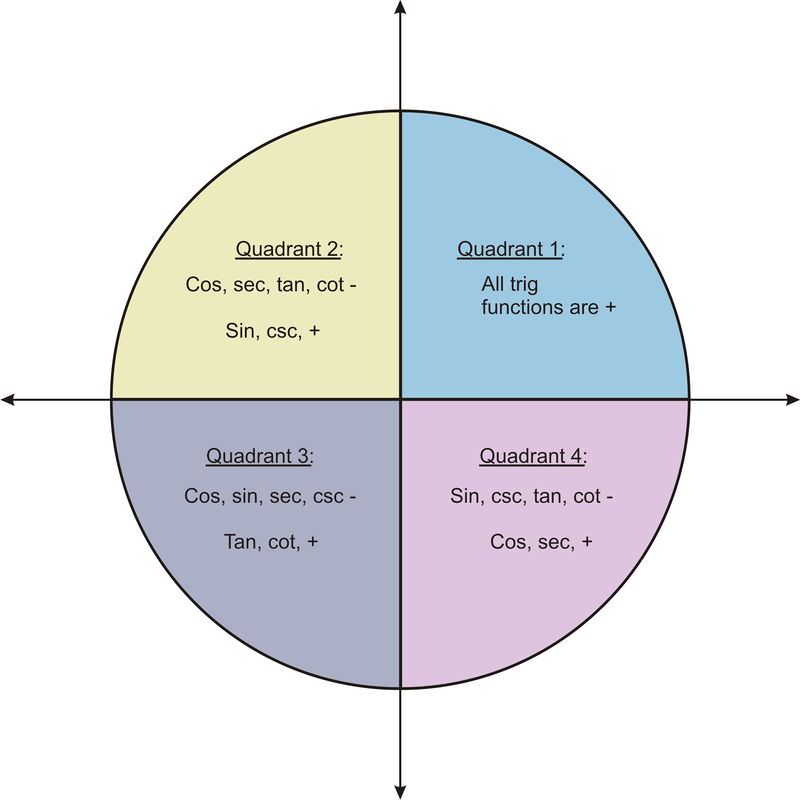


Domain Range And Signs Of Trigonometric Functions Read Trigonometry Ck 12 Foundation
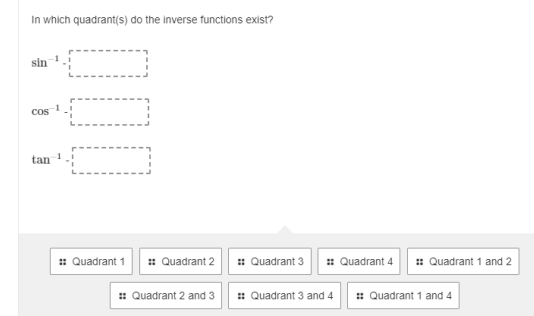


Answered In Which Quadrant S Do The Inverse Bartleby
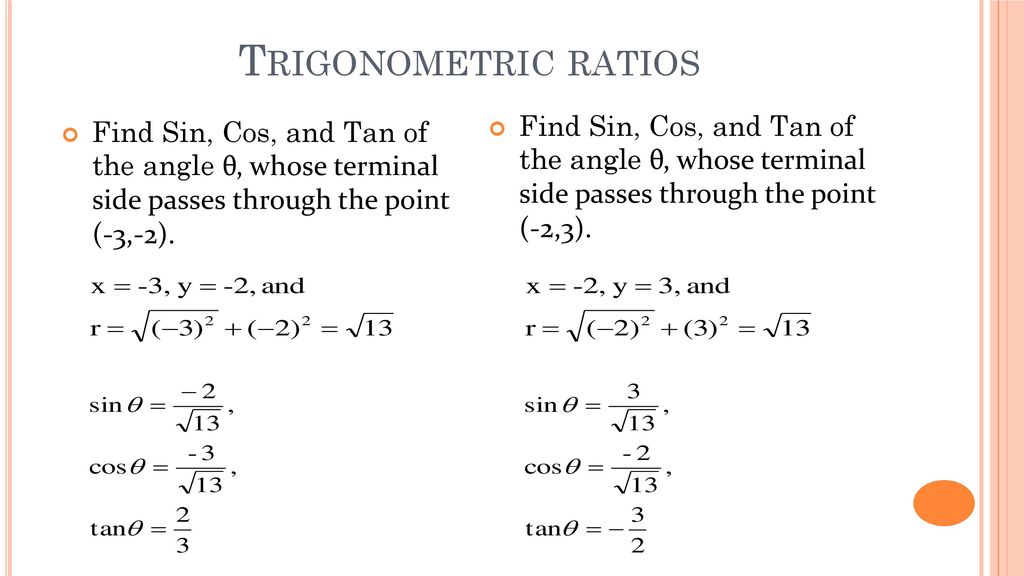


Chapter 6 Trigonometry Ppt Download
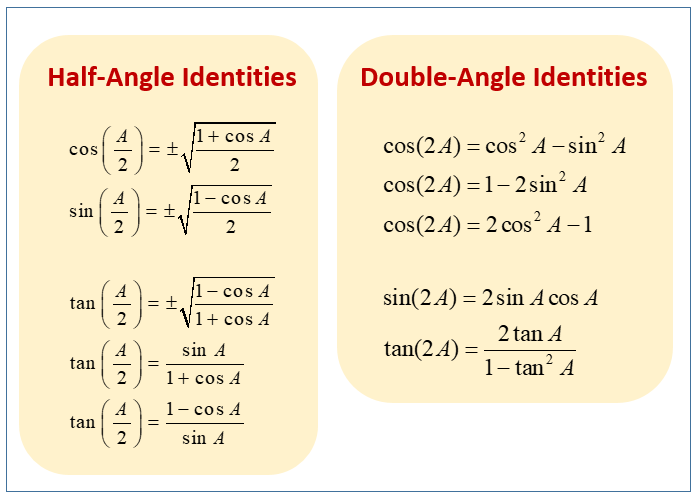


Half Angle Or Double Angle Examples Examples Solutions Videos Worksheets Games Activities
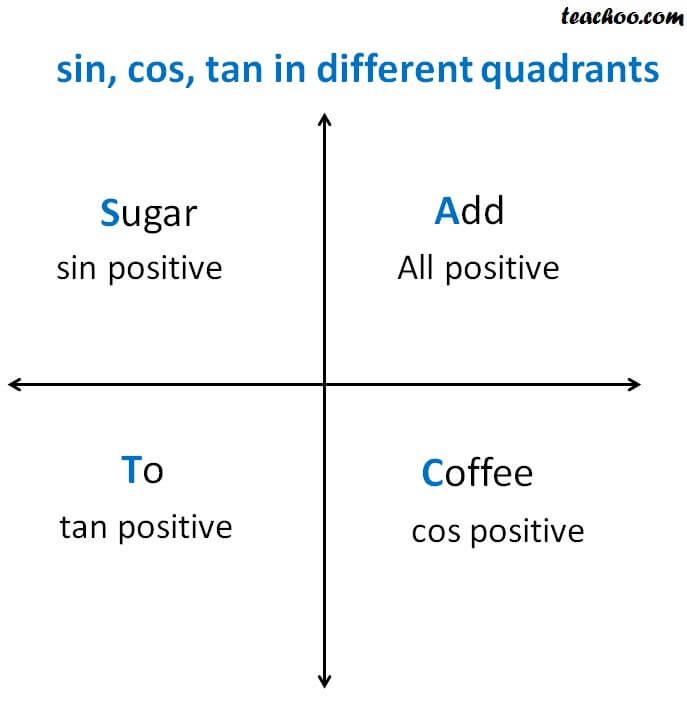


Signs Of Sin Cos Tan In Different Quadrants Finding Value Of Trign
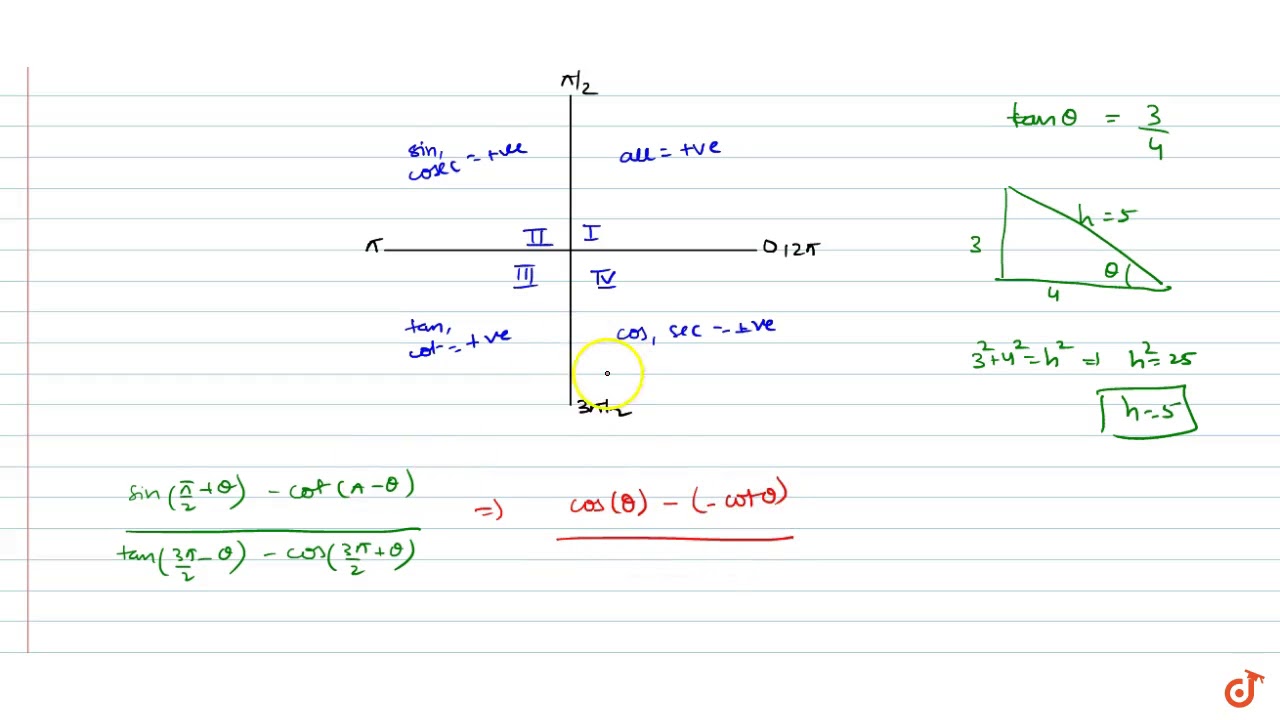


If Tan Theta 3 4 And Theta Is Not In First Quadrant Then Sin Pi 2 Theta Cot Pi Theta Youtube



Content The Four Quadrants



Ex 3 2 1 Find Values Of Other Five Trigonometric Functions If Cos X



Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants


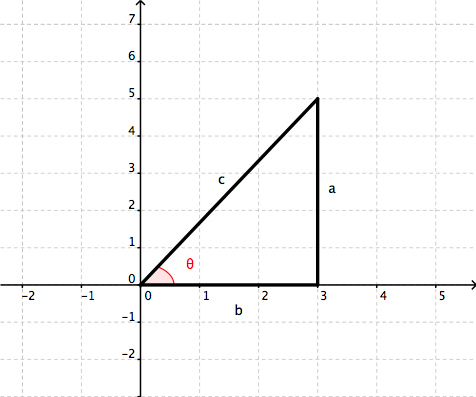
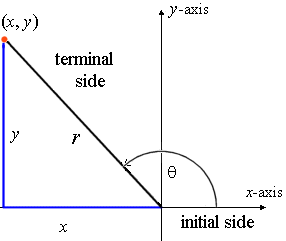
Trigonometric Functions Of A General Angle


If Sin Of Theta Equals 3 8 And Theta Is In Quadrant Ii What Are Cos Tan Csc Cot And Sec Of Theta Socratic


42 Printable Unit Circle Charts Diagrams Sin Cos Tan Cot Etc


5 Signs Of The Trigonometric Functions


Trigonometric Ratios Solutions Examples Videos



Where Are Quadrant 1 2 3 4 Page 1 Line 17qq Com
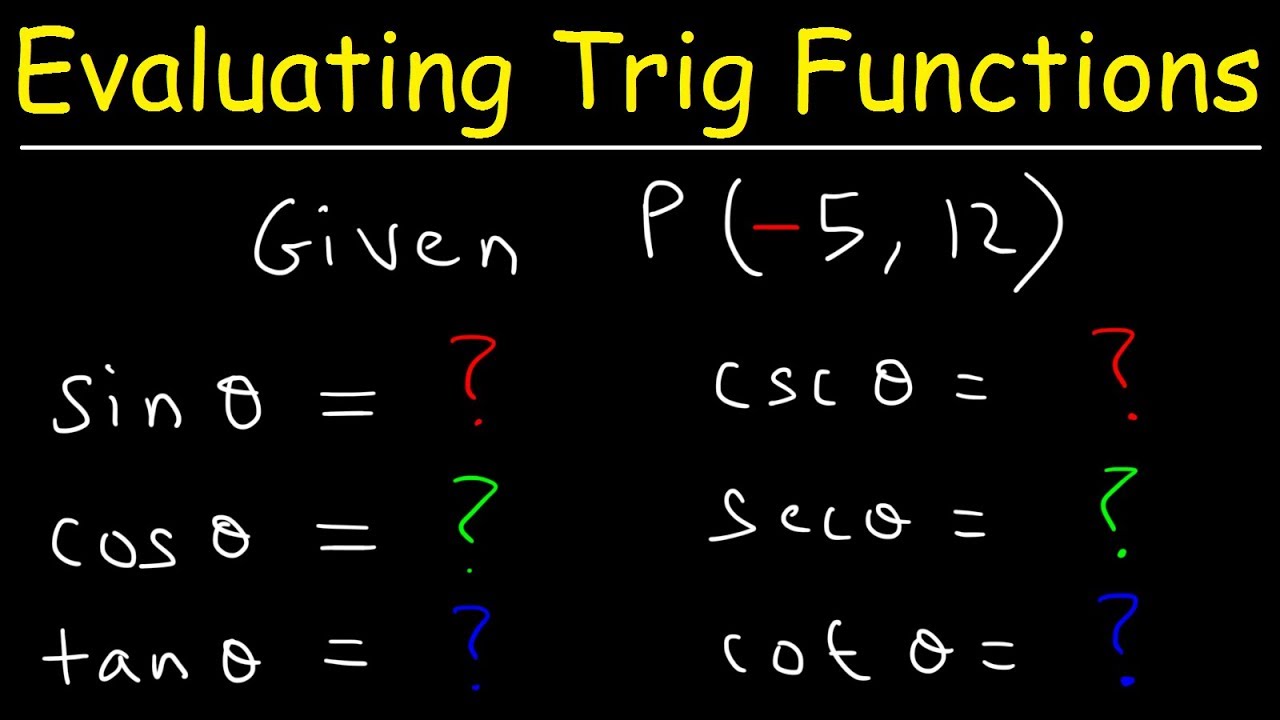


Evaluating Trigonometric Functions Given A Point On The Terminal Side Trigonometry Youtube
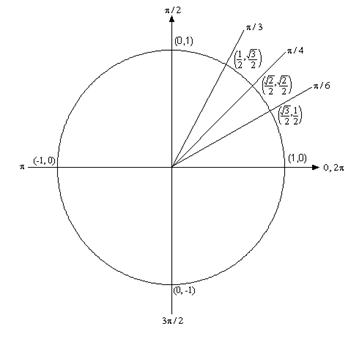


Algebra Trig Review
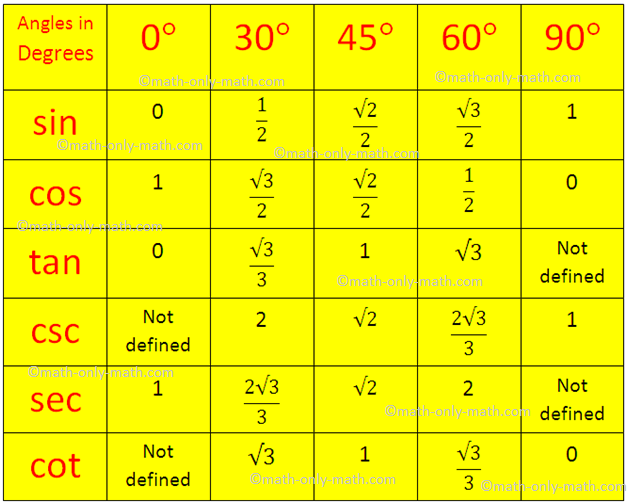


Trigonometrical Ratios Table Trigonometric Standard Angles Standard



Defining Ratios In The Cartesian Plane Trigonometry Siyavula



Trigonometric And Geometric Conversions Sin A B Sin A B Sin Ab
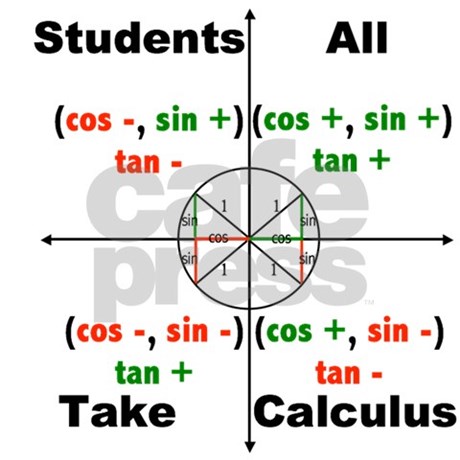


If Cos 0 And Sin 0 What Quadrant Is It In Socratic
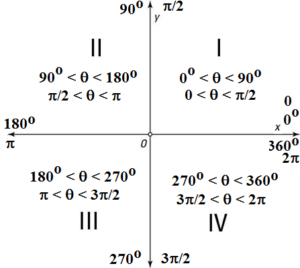


Signs Of Trigonometric Ratios In Diffrent Quadrants Formed Due To Axes



Solved 3 Given Sin U Where U Is In Quadrant 1 And Sec Chegg Com



Easy Way Of Memorizing Values Of Sine Cosine And Tangent Mathematics Stack Exchange


If Tan 8 Is Positive And Sin 8 Is Negative In Which Quadrant Does 8 Lie Quora


The Trigonometry Functions



Solved Find Sin Theta Cos Theta 3 4 Theta In Quadrant Chegg Com
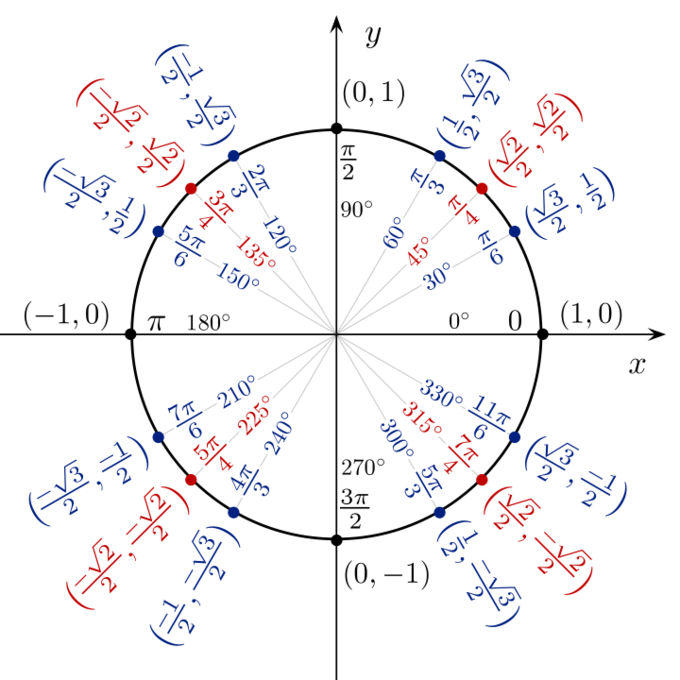


Trigonometric Functions And The Unit Circle Boundless Algebra
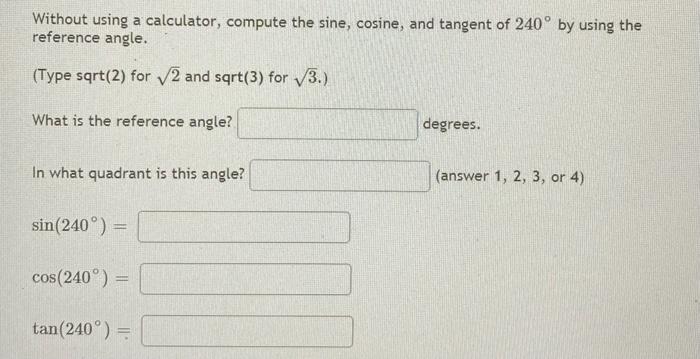


Solved Without Using A Calculator Compute The Sine Cosi Chegg Com



The Unit Circle Reference Angles And Trigonometry Ppt Video Online Download
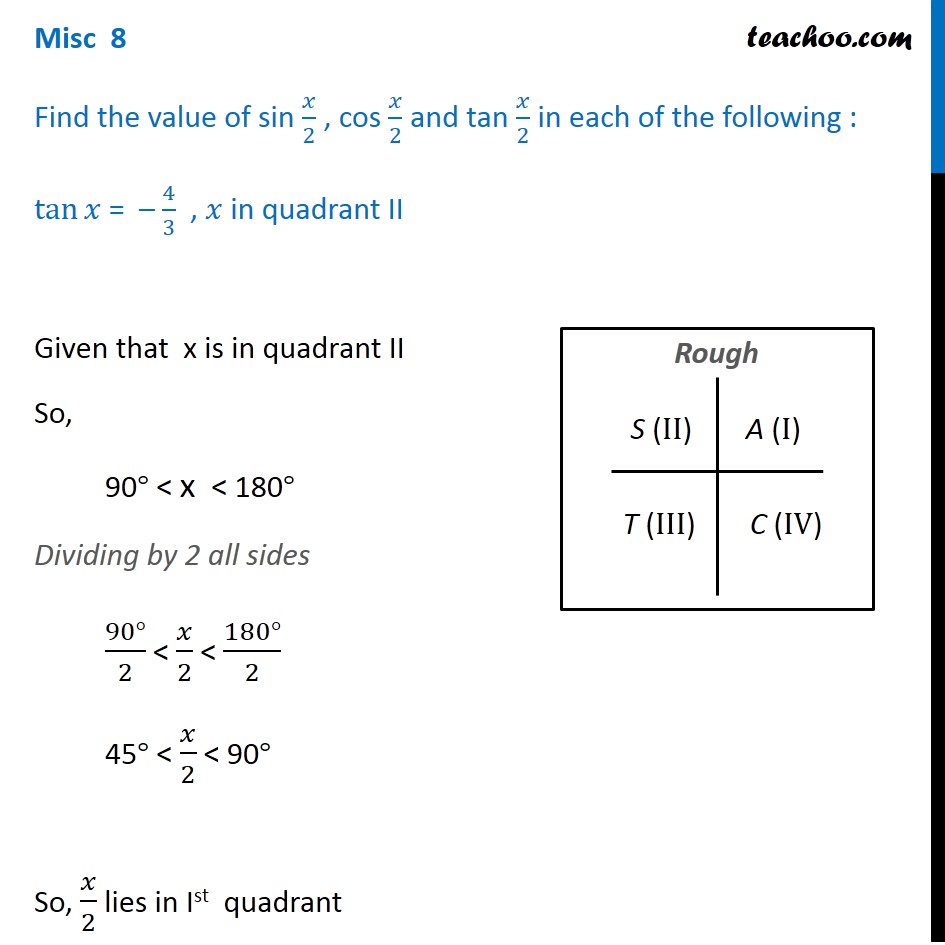


Misc 8 Tan X 4 3 Find Sin X 2 Cos X 2 And Tan X 2


Trigonometry Trigonometric Functions Functions In Quadrants Sparknotes



Similarity Trigonometric Functions The Unit Circle Similarity Same



Solved From The Information Given Find The Quadrant In W Chegg Com



Lesson 41 Trigonometric Equations Ib Math Sl Santowski


What Trig Functions Are Positive In Which Quadrants Socratic



What Is Quadrant 1 2 3 4 Page 1 Line 17qq Com


Trigonometric Functions Of A General Angle



Quadrants Sin Cos Tan Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Misc 10 Sin X 1 4 Find Sin X 2 Cos X 2 Tan X 2 Chapter 3


The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl


Sin Cos Tan Potentwise



Trig Practice Set



Easy Way Of Memorizing Values Of Sine Cosine And Tangent Mathematics Stack Exchange


Tangent Function Tan Graph Solved Examples Cuemath


7 The Inverse Trigonometric Functions



Trigonometry


Relating Trigonometric Functions Trigonometry Socratic


If Csc Theta 4 3 What Is The Sin Cos Tan Sec And Cot Socratic



Answered Without Using A Calculator Compute The Bartleby



Exam 2 Review Key



Chapter 6 Trigonometry Section 6 4 Trigonometric Functions



Where Are Quadrant 1 2 3 4 Page 5 Line 17qq Com
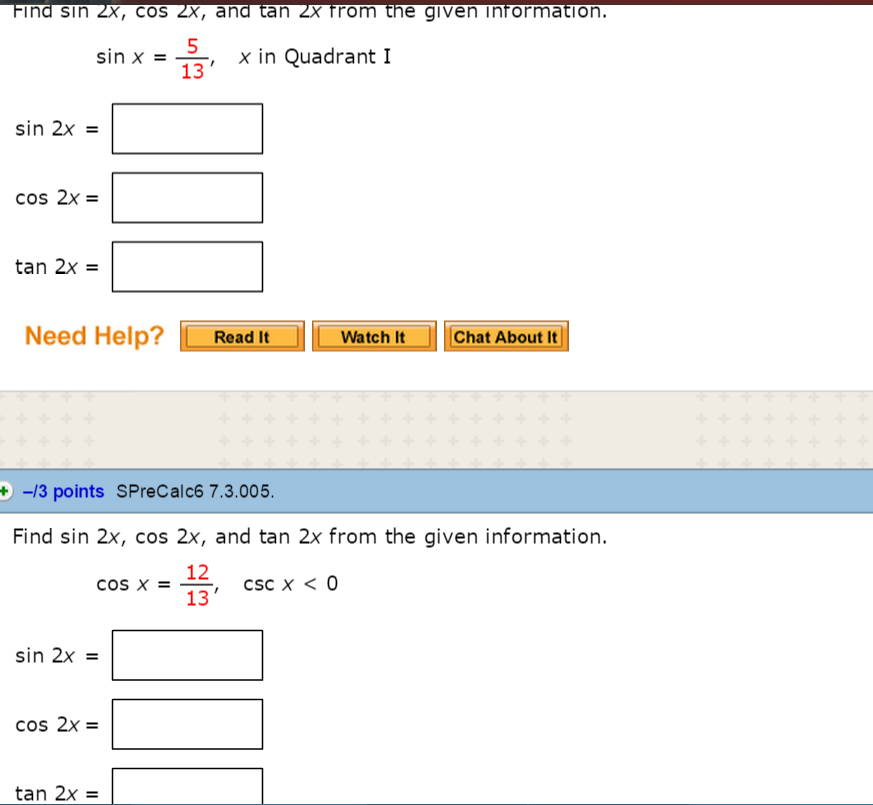


Solved Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x From The Given Inf Chegg Com



If Cot Theta 3 4 And Theta Is Not In The Second Quadrant Then 5 Sin Theta 10 Cos Theta Youtube


Inverse Trigonometric Functions Precalculus Ii


Biomath Trigonometric Functions


Trigonometric And Geometric Conversions Sin A B Sin A B Sin Ab


Tips Tricks And Power Tools How To Memorize Sine Cosine And Tangents Of 0 30 45 60 And 90 Degrees


Solved The Terminal Point P X Y Determined By A Real Number T Is Given Find Sin T Cos T And Tan T 1 2v 2 Sin T Cos T Tan T The Te Course Hero


Sum And Difference Identities Precalculus Ii



5 3 Trigonometric Ratios For Angles Greater Than 90o Ppt Download


Exact Trig Values
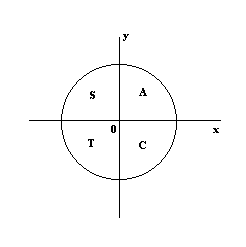


Sin Cos And Tan Mathematics A Level Revision


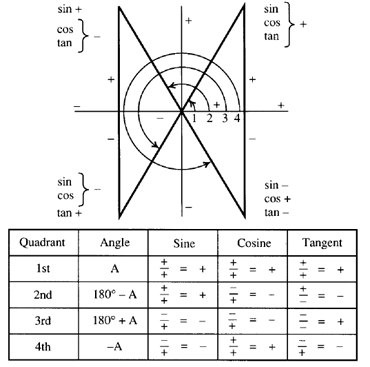
Signs Of Sin Cos Tan In Different Quadrants Finding Value Of Trign
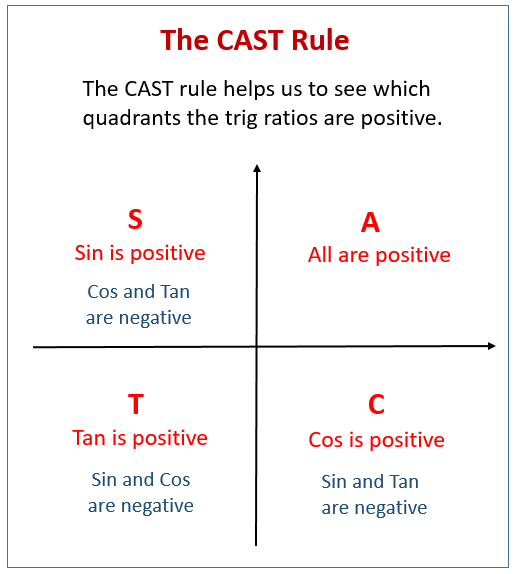


Finding Exact Trig Values Solutions Examples Videos Worksheets Games Activities



Mnemonics In Trigonometry Wikipedia



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿